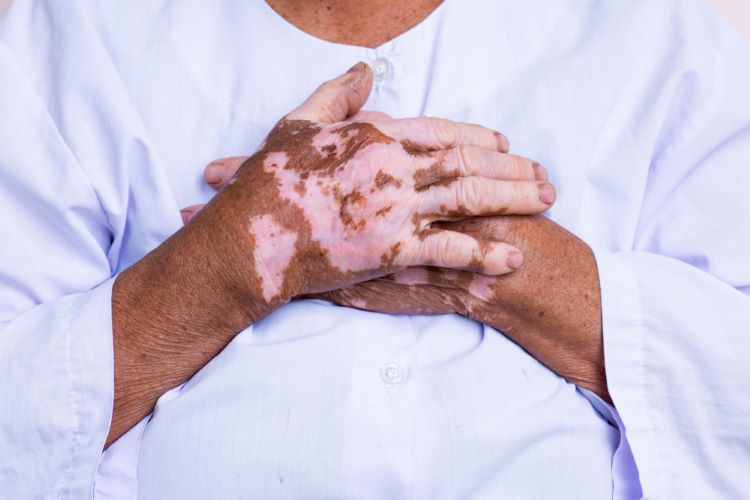
Vitiligo treatment gets positive CHMP opinion
Posted: 24 February 2023 | Catherine Eckford (European Pharmaceutical Review) | No comments yet
If approved, the cream formulation of the JAK inhibitor ruxolitinib will be the first treatment for repigmentation in non-segmental vitiligo available in the European Union.


The Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) has issued a positive opinion recommending approval of ruxolitinib cream (Opzelura™) for non-segmental vitiligo with facial involvement in people over 12 years old.
“With no centrally approved treatment option currently available in the EU, this positive opinion marks a significant milestone for the vitiligo community,” explained Dr Steven Stein, Chief Medical Officer, Incyte. When approved, this will be the first approved vitiligo therapy available in the EU for this indication.
About ruxolitinib cream
Ruxolitinib cream is a novel cream formulation of Incyte’s selective Janus kinase (JAK)1/JAK2 inhibitor ruxolitinib, approved by the US Food & Drug Administration (FDA) for topical treatment of nonsegmental vitiligo in patients 12 years of age and older. It is the first and only treatment for repigmentation approved in the US.
What led to recommendation of the JAK inhibitor?
The CHMP’s opinion was based on data from two pivotal Phase III clinical trials (TRuE-V1 and TRuE-V2) evaluating ruxolitinib cream versus vehicle (non-medicated cream) in more than 600 people with non-segmental vitiligo, aged 12 and older. Results from the TRuE-V1 and TRuE-V2 trials were recently published in The New England Journal of Medicine.
Key results from the Phase III trials for vitiligo
Significant improvements in facial and total body repigmentation versus vehicle were observed as shown by the number of patients reaching the facial and total body Vitiligo Area Scoring Index (F-VASI-T-VASI) endpoints at Week 24 compared to vehicle. A higher proportion of patients responded at Week 521.
- In TRuE-V1, the percentage of patients with an F-VASI75 response at week 24 was 29.8 percent in the ruxolitinib-cream group and 7.4 percent in the vehicle group
- In TRuE-V2, the percentages were 30.9 percent and 11.4 percent, respectively.
#News: @EMA_News has issued a positive opinion for an Incyte-discovered therapy for patients with #vitiligo. #CHMP
— Incyte (@Incyte) February 24, 2023
Vitiligo
Vitiligo is a chronic autoimmune disease characterised by skin depigmentation resulting in patchy loss of skin colour from the progressive destruction of pigment-producing cells known as melanocytes. Overactivity of the JAK signalling pathway is believed to drive inflammation involved in the pathogenesis and progression of vitiligo.
Related topics
Biopharmaceuticals, Clinical Development, Drug Development, Drug Safety, Therapeutics