Scientists use RFID chips to track biological samples
Posted: 1 June 2018 | European Pharmaceutical Review | No comments yet
Researchers in the U.S. and Japan want to use radio frequency identification (RFID) chips keeping track of organoids…


Researchers in the U.S. and Japan want to use radio frequency identification (RFID) chips keeping track of organoids — samples of human tissue that mimic pieces of organs and are grown from stem cells. The organoids the researchers embedded with RFID chips functioned normally and withstood extreme conditions, suggesting that they could be a useful way to organise and identify the large quantities of organoids that are often needed in experimental situations.
“This kind of multidisciplinary approach potentially offers a disruptive way forward: the idea is to combine organoids with digital technologies to advance drug testing and transplantation,” says senior author Takanori Takebe, a clinician and researcher at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, Tokyo Medical and Dental University, and Yokohama City University.
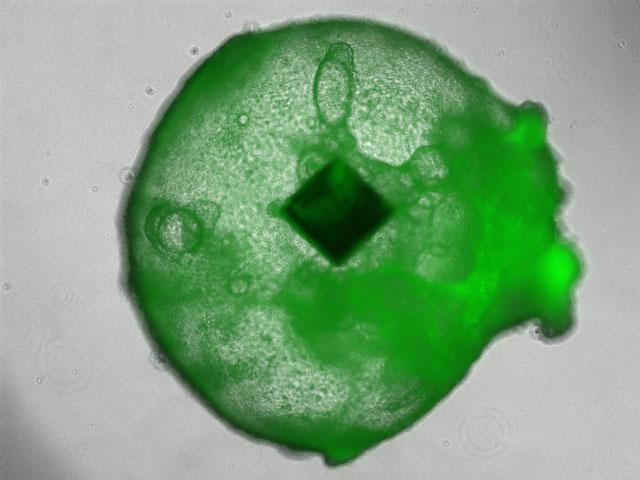

This image shows a human liver organoid with an embedded RFID microchip. ( Kimura et al./iScience)
Human organoids are a promising avenue for research into human development and disease because they replicate the structure, function, and phenotype of our organs in miniature in the lab. Grown from human induced pluripotent stem cells, they divide, differentiate, and self-assemble according to the growth programs of their corresponding organs. And particularly in medicine, they can illustrate the effects of certain drugs on our organs in ways that more traditional cell cultures cannot.
The idea of embedding microchips into human organoids seemed like a natural fit to Dr Takebe, who has worked extensively with RFID chips in health contexts. The chips could be used to sense, record, and track interesting changes live in large quantities of organoids at once–and because of cells self-assembled into 3D structures during the growth process of an organoid, he thought it might be possible for the microchips to be naturally integrated into the organoids as they were growing. “Introducing the chips by forceful methods like injection is extremely toxic to organoids, so we leveraged the organoid’s natural self-cavitation power to integrate the microchips so that we could prevent tissue damage and destruction,” he says.
To test this procedure, he and his team grew hybrid liver organoids containing cheap, commercially available RFID chips the size of grains of sand. They found that 95% of their 96 test organoids successfully incorporated the chip. The organoids were undamaged by the procedure: they were shaped normally, secreted by normal liver proteins, and transported bile as expected. “There were almost no differences, surprisingly,” says Dr Takebe.
The RFID chips, which are known for their durability, also functioned as expected. Hybrid organoids grown from stem cells of donors with fatty liver disease could be identified by RFID in a pool of organoids from a variety of donors. And the chips also stood up to a number of tests of the kinds of conditions they might need to survive in order to be useful in research: they and their organoids still functioned normally after being frozen and thawed for cryopreservation, at temperatures of nearly minus 200 degrees Celsius, after being embedded in paraffin, and at a range of different pHs.
Dr Takebe acknowledges that there are still limitations to this approach. More work needs to be done to scale up the production of these hybrid organoids, and he and his team are currently working to develop a system that could scan the radio frequency and fluorescence of an organoid at the same time. He also hopes that other kinds of microchips could be integrated into organoids in the future and that RFID chips with sensing technologies could be used to record real-time data about the organoids. “My lab’s focus is completely biological, so some of these challenges are things we cannot resolve alone. But with collaboration between experts in different fields, and especially given how rapidly technology is evolving, I believe that we can and will solve them,” he says.
The work appears in the journal iScience.
Related topics
Related organisations
Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center, Dental University, Yokohama City University








