Contract Manufacturing Organisations poised for great opportunities
Posted: 7 April 2008 | Dr. Amarpreet S Dhiman, Drug Discovery Technologies, Healthcare (EMEA) and Industry Analyst, Drug Discovery and Clinical Diagnostics Frost & Sullivan and Programme Leader | No comments yet
In the highly competitive contract manufacturing outsourcing (CMO) market the industry is on the rise with pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies targeting their resources towards marketing, rather than production and drug discovery. Pharmaceutical and biopharmaceutical companies are faced with the need to outsource the manufacture of their products for a variety of reasons.
In the highly competitive contract manufacturing outsourcing (CMO) market the industry is on the rise with pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies targeting their resources towards marketing, rather than production and drug discovery. Pharmaceutical and biopharmaceutical companies are faced with the need to outsource the manufacture of their products for a variety of reasons.
In the highly competitive contract manufacturing outsourcing (CMO) market the industry is on the rise with pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies targeting their resources towards marketing, rather than production and drug discovery. Pharmaceutical and biopharmaceutical companies are faced with the need to outsource the manufacture of their products for a variety of reasons.
Some of the main reasons include start-up companies that frequently do not have the facilities or expertise necessary to produce the type or quantities of drugs or biologics that are necessary for performing pre-clinical and clinical studies of investigational new drugs. Furthermore, established companies with FDA-approved drugs or biologics may not have manufacturing facilities that comply with current good manufacturing practices, or they may not have the adequate capacity to fulfil the commercial demands for their products and may desire manufacturing back-ups. Although the technical details that are part of any contract manufacturing agreement will vary depending on the nature of the project, a mutually satisfactory agreement that anticipates issues that are likely to arise is the key to the production of acceptable product and the long-term success of the relationship. The need for the services of CMOs has given rise to a vibrant industry that is likely to grow as that need increases. This shift in focus towards contract manufacturing also includes cost efficiency, lack of in-house expertise with the changing technology and to have advantage of the time-to-market drugs.
The European pharmaceutical contract manufacturing market is the second largest globally and differs from its US counterpart with respect to its business model. However, Europe is ahead of other regions in outsourcing production owing to a greater need for cutting health care expenditure. Health care budgets in most European countries are spiralling out of control and their respective governments are looking to reduce health care budgets that are putting pressure on companies to lower their drug prices. In contrast, the US pharmaceutical contract manufacturing market is the largest in the world and has been at the forefront of the industry in terms of technology offerings as well as value-added services provided to clients. The US has the advantage as increasing pressure from governments and managed care organisations request to lower drug costs, which will create more outsourcing opportunities. The core client base of the European CMOs constitutes generic drug companies, while branded pharmaceuticals form the core client base in the US. In recent years, the volume of generic drug sales has been increasing rapidly in Europe, whereas the outsourcing of branded pharmaceuticals in Europe has been growing at a slower rate due to the lack of any capacity constraint with pharmaceutical companies. A large number of branded pharmaceuticals have moved towards maturity and late growth stages in the product life cycle. Hence, utilisation levels of these plants are likely to grow to unsustainable levels. This makes outsourcing a viable option.
Some of the major technology trends within the CMO industry include the following:
- Manufacturing of biopharmaceutical
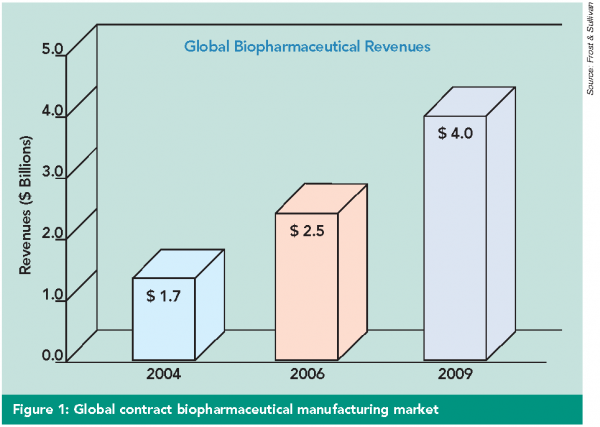
Current in late phases of development, several biopharmaceutical products such as sterile injectables, especially oncology products are likely to be approved and enter the market. Since biopharmaceutical companies are looking to invest in research and development, there is likely to be a huge demand for manufacturing capacity for sterile vials and syringes. This trend is likely to drive the injectables segment worldwide. Biologics manufacturing has also shown a steady but solid growth in recent years with contract manufacturers accounting for 20-30% industry wide manufacture of biopharmaceuticals (Figure 1). - Cytotoxics
An area which has not been given much importance in the past, cytotoxics, has immense opportunity for growth for contract manufacturers. In spite of new innovative treatments for cancer, chemotherapy continues to remain the chief treatment option for major tumours. The demand for manufacturing of cytotoxics is expected to be on the rise in forthcoming years. - Flexible manufacturing plants
By investing in manufacturing plants, contract manufacturers can generate cash flows for a sufficient period of time to offset the cost of the plant, fund newer projects and upgrade the facility for technology and skill set of employees. By building a manufacturing plant that is designed to be flexible to accommodate the changing needs of a client (pharmaceutical companies), contract manufacturers can save on higher investments in the future and can also ensure sufficient cash flow from existing operations. - Automation
A significant trend in the future would be the incorporation of automation along with the marriage of miniaturisation and cutting-edge robotics. The increasing number of high-potency drugs, the release of which may prove to be hazardous to employees, is likely to drive the integration of automation in manufacturing plants. Automation also reduces the need for continuous checking of verification of labour, increases the productivity and ensures reliability and consistency. Whilst this does not necessarily mean job reductions, it could simply imply use of remote control systems wherein employees may control the activities from outside the production area. Automation in analytical technology could be utilised for automatic sampling of production on a preset basis and could thereby effectively monitor critical processes. This eliminates the need to use manual sampling, which could be time consuming as well as potentially hazardous.
Conclusions
The pharmaceutical industry is moving to a structure where a handful of multinationals supported by an army of contract researchers and contract manufacturers will control most of the global pharmaceutical market. Indeed, outsourcing seems to be an obvious solution for companies to solve the problems at hand and at the same time exploit the potential of new drug discovery technologies. It is a great challenge to successfully manage the outsourcing relationship and generate value from it.

Background
Frost & Sullivan, a global growth consulting company, has been partnering with clients to support the development of innovative strategies for more than 40 years. The company’s industry expertise integrates growth consulting, growth partnership services, and corporate management training to identify and develop opportunities. Frost & Sullivan serves an extensive clientele that includes Global 1000 companies, emerging companies, and the investment community by providing comprehensive industry coverage that reflects a unique global perspective and combines ongoing analysis of markets, technologies, econometrics, and demographics.
Dr. Amarpreet S Dhiman
Drug Discovery Technologies, Healthcare (EMEA) and Industry Analyst, Drug Discovery and Clinical Diagnostics Frost & Sullivan and Programme Leader
Amarpreet joined Frost & Sullivan as research analyst in 2004. Working with top multinational companies and communicating with top level healthcare company executives in the drug discovery and clinical diagnostics field, Amarpreet is directly involved in project delivery, from launch to quality control phases according to a stringent production timeline.
In addition to writing a number of commercially penetrating articles and participating in several international seminars and conferences, he has finished profiling fast-growing emerging markets in the drug discovery and clinical diagnostics field, focusing on the whole value chain of the drug discovery and development process.
Amarpreet holds a Ph.D. in Dental Prosthetics from Queen Mary University (London) in addition to a Master’s Degree in Biomedical Engineering from Imperial College (London), and has published many papers in peer-reviewed scientific journals.