Cancer detection using light-emitting nanoparticles
Posted: 12 December 2017 | Dr Zara Kassam (European Pharmaceutical Review) | No comments yet
Light-emitting nanoprobes can detect cancer early and track the spread of tiny tumours…


Using light-emitting nanoparticles scientists have invented a highly effective method to detect tiny tumours and track their spread, potentially leading to earlier cancer detection and more precise treatment.
The technology could improve patient cure rates and survival times.
“We’ve always had this dream that we can track the progression of cancer in real time, and that’s what we’ve done here,” said Prabhas V. Moghe, a corresponding author of the study and distinguished Professor of Biomedical Engineering and Chemical and Biochemical Engineering at Rutgers-New Brunswick. “We’ve tracked the disease in its very incipient stages.”
The study shows that the new method is better than magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and other cancer surveillance technologies. The research team included Rutgers’ flagship research institution (Rutgers University-New Brunswick) and its academic health centre (Rutgers Biomedical and Health Sciences, or RBHS).
“The Achilles’ heel of surgical management for cancer is the presence of micro-metastases. This is also a problem for proper staging or treatment planning. The nanoprobes described in this paper will go a long way to solving these problems,” said Dr Steven K. Libutti, director of Rutgers Cancer Institute of New Jersey. He is senior vice president of oncology services for RWJBarnabas Health and vice chancellor for cancer programs for Rutgers Biomedical and Health Sciences.
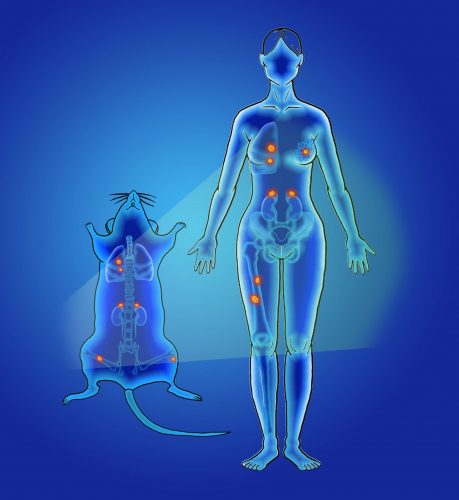

This illustration shows how human breast cancer cells in a mouse model were “chased” with novel rare earth nanoscale probes injected intravenously. When the subject is illuminated, the probes glow in an infrared range of light that is more sensitive than other optical forms of illumination. In this case, the probes show the spread of cancer cells to adrenal glands and femur (thigh) bones.
CREDIT : Harini Kantamneni and Professor Prabhas Moghe/Rutgers University New Brunswick
The ability to spot early tumours that are starting to spread remains a major challenge in cancer diagnosis and treatment, as most imaging methods fail to detect small cancerous lesions. But the Rutgers study shows that tiny tumours in mice can be detected with the injection of nanoprobes, which are microscopic optical devices, that emit short-wave infrared light as they travel through the bloodstream – even tracking tiny tumours in multiple organs.
The nanoprobes were significantly faster than MRIs at detecting the minute spread of tiny lesions and tumours in the adrenal glands and bones in mice. That would likely translate to detection months earlier in people, potentially resulting in saved lives, said Vidya Ganapathy, a corresponding author and Assistant Research Professor in the Department of Biomedical Engineering.
“Cancer cells can lodge in different niches in the body, and the probe follows the spreading cells wherever they go,” she said. “You can treat the tumours intelligently because now you know the address of the cancer.”
The technology could be used to detect and track the 100-plus types of cancer, and could be available within five years, Moghe said. Real-time surveillance of lesions in multiple organs should lead to more accurate pre- and post-therapy monitoring of cancer.
“You can potentially determine the stage of the cancer and then figure out what’s the right approach for a particular patient,” he said.
In the future, nanoprobes could be used in any surgeries to mark tissues that surgeons want to remove, the researchers said. The probes could also be used to track the effectiveness of immunotherapy, which includes stimulating the immune system to fight cancer cells.
The study has been published online in Nature Biomedical Engineering.
Related topics
Clinical Development, Clinical Trials, Imaging, Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), Nano particles, Particle Sizing
Related organisations
Rutgers Biomedical and Health Sciences, Rutgers University-New Brunswick