Address the time-to-result challenge posed by short shelf-life radiopharmaceuticals.
20 November 2025 | 3:00 PM GMT | FREE Virtual Panel Discussion
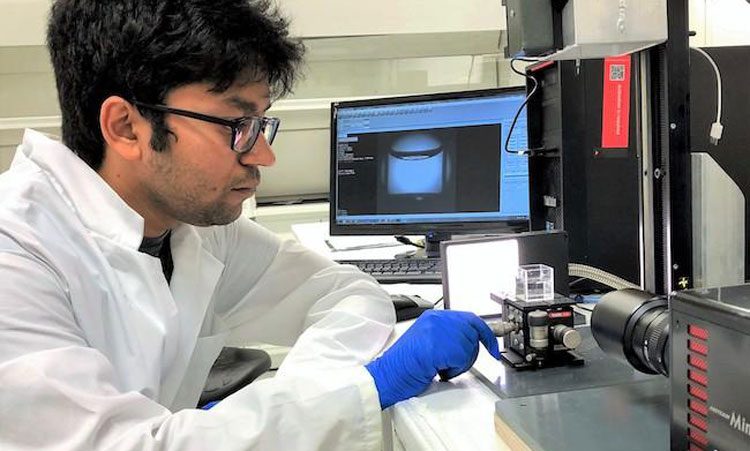
This webinar showcases the Growth Direct System; an RMM (Rapid Microbial Method) that improves on traditional membrane filtration, delivering increased accuracy, a faster time to result, enhanced data integrity compliance, and more control over the manufacturing process.
Key learning points:
- Understand the benefits of full workflow microbiology quality control testing automation in radiopharmaceutical production
- Learn about ITM’s implementation journey and considerations when evaluating the technology
- Find out how the advanced optics and microcolony detection capabilities of Growth Direct® technology impact time to result (TTR).
Don’t miss your chance to learn from experts in the industry – Register for FREE