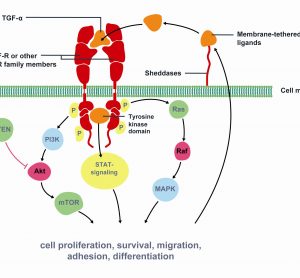
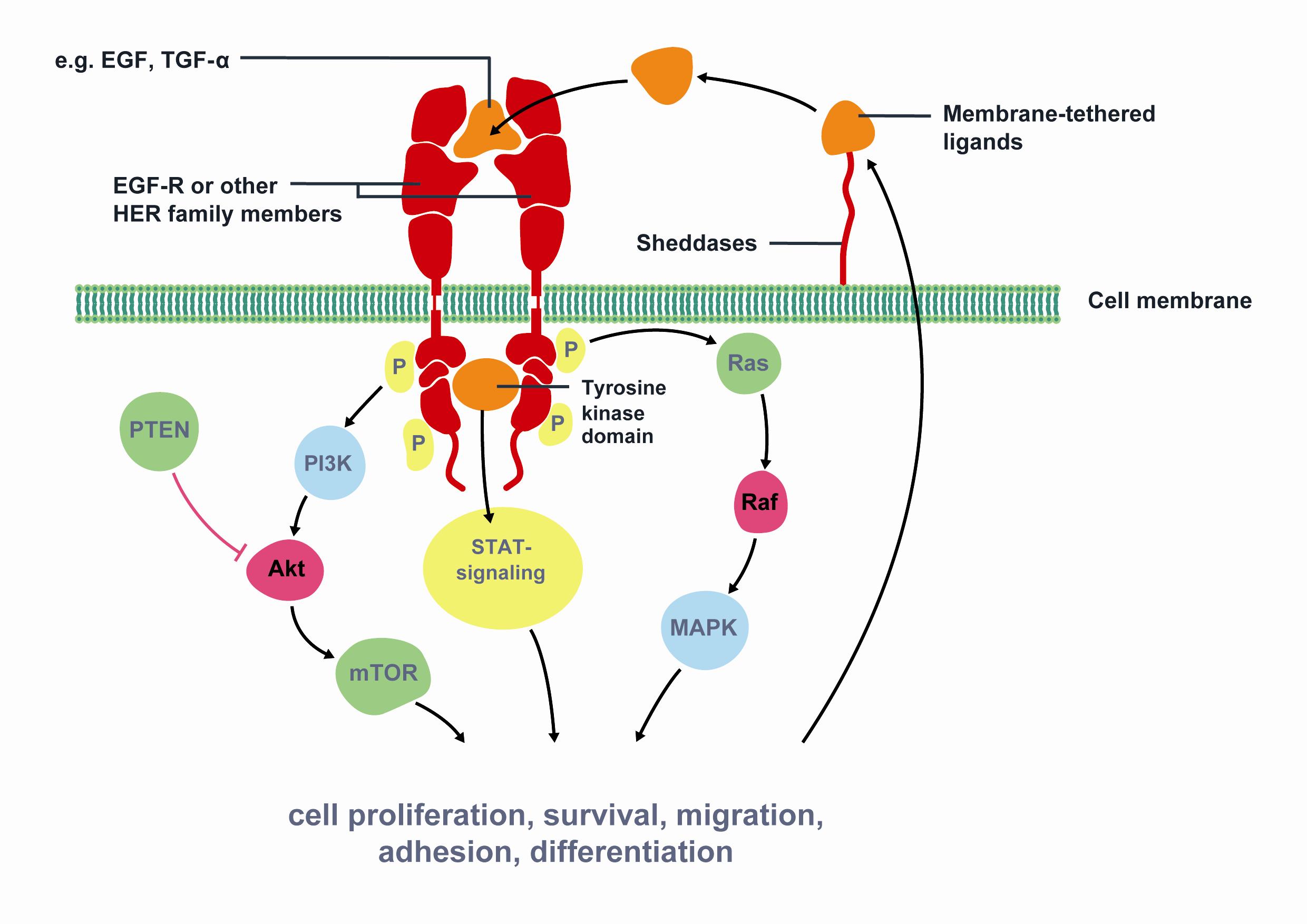
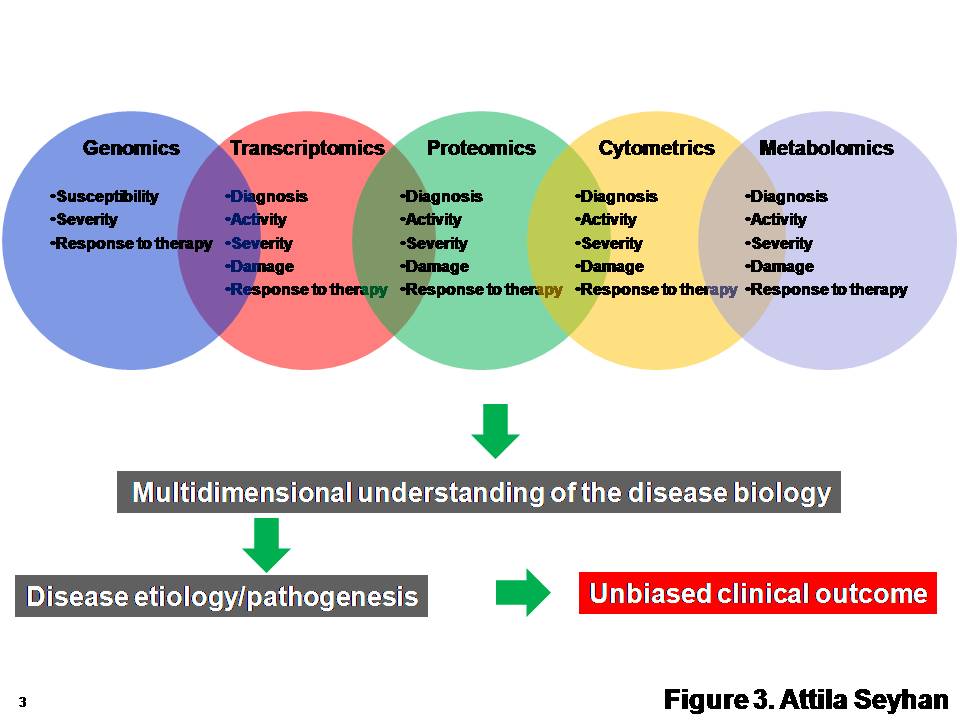
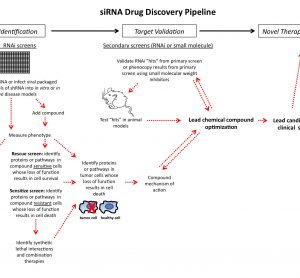
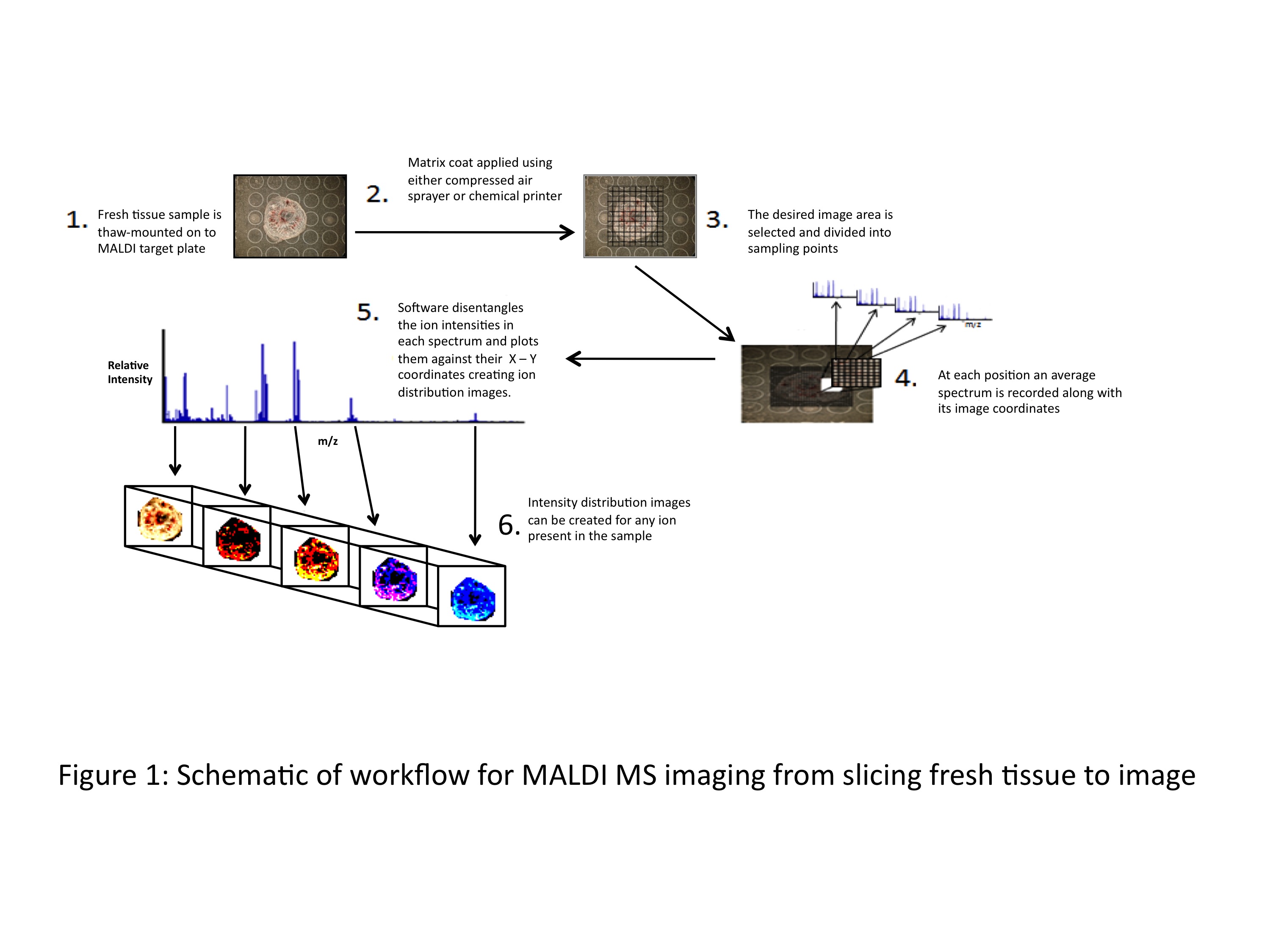
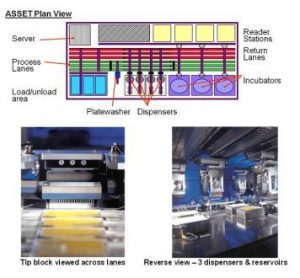
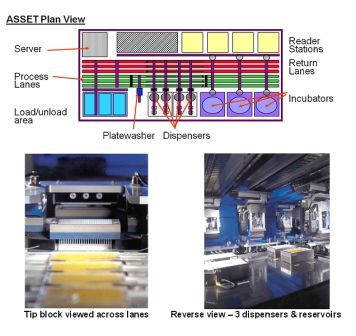
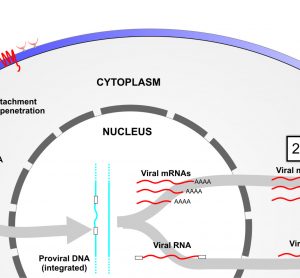
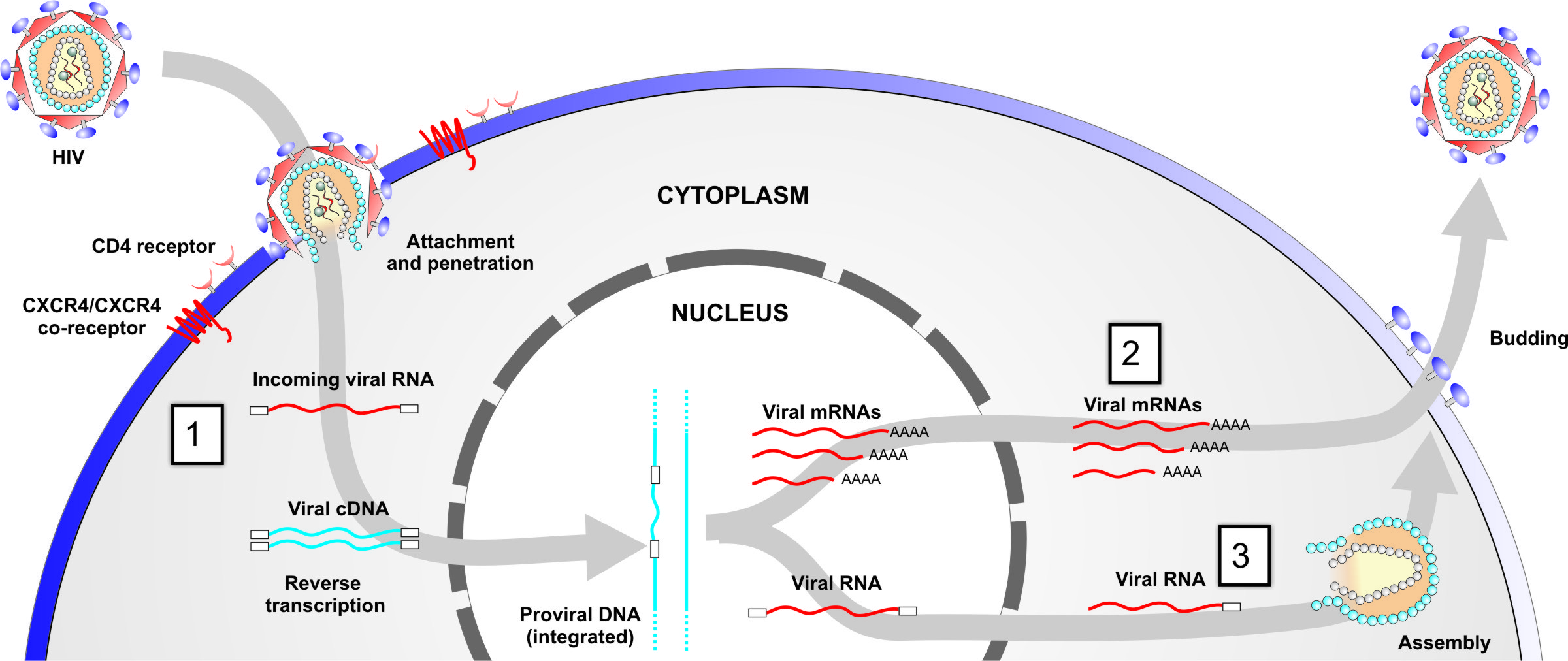
Targeted therapies in lung cancer and Biomarkers
16 December 2010 | By Wolfgang M. Brueckl & Joachim Ficker, Department of Internal Medicine 3, Lung Cancer Center and Thomas M. Mundel, Roche Parma AG
Despite innumerable clinical studies in the past three decades with lots of traditional chemotherapeutical drugs and drug combinations, survival in lung cancer has increased by far less than other entities. Research now focuses on inhibitors of tyrosine kinases which have been shown to have a central role in the development…