Using fatty acids in oral formulations to improve drug delivery
Posted: 6 April 2020 | Victoria Rees (European Pharmaceutical Review) | No comments yet
Researchers have used triglyceride fatty acids to develop an oral formulation for drugs that are usually injected or taken intravenously.

Nanomedicine researchers report that triglycerides could effectively transport oral medication in the body and eliminate the need for some injections or IV treatment.
The team, from Houston Methodist, US, say that this new drug delivery system for a diabetes drug resulted in approximately 25 percent absorption in mice models. According to the researchers, their findings may pave the way for oral delivery of more biological drugs, similar to those used to treat rheumatoid arthritis and other autoimmune diseases.
“We know the human body can absorb fatty acids, so we decided to chemically link biological drug molecules to fatty acids to see how well these drugs are absorbed into the gastrointestinal system. It turns out that our ‘transporter approach’ was effective,” said Dr Haifa Shen, professor of nanomedicine at Houston Methodist Research Institute.
After designing a platform where a peptide-based drug used to treat diabetes mellitus was chemically linked to fatty acids, Shen and the team packaged the resulting combination in a nanoparticle that was resistant to gastric acids in the stomach. Once inside the small intestine, the drug molecules were released from the nanoparticle and the mice absorbed 24.8 percent of the drug dosage.
The majority of small molecule drugs are prepared in tablets and given orally. However, biological drugs, like those to treat diabetes, cannot sustain the harsh environment in the gastrointestinal tract, which includes gastric fluids and digestive enzymes in the stomach. The only option has been IV infusion or injections, which are more costly than oral drugs and pose compliance challenges for many patients who struggle with inconvenient appointments and the high cost of treatment.
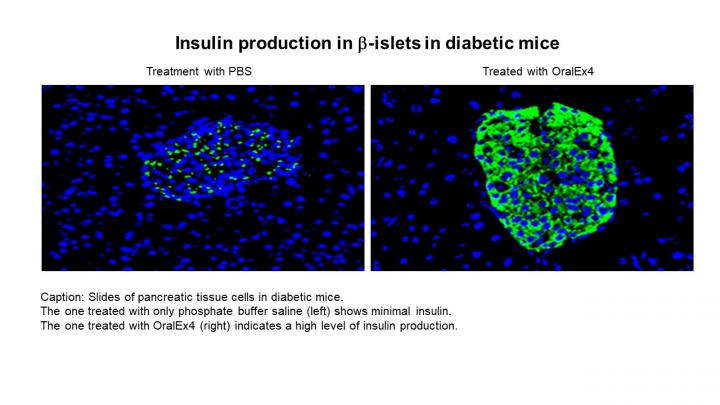

Houston Methodist researchers designed a platform where a diabetes drug was chemically linked to fatty acids and then packaged in a nanoparticle resistant to the stomach’s gastric acids. Once inside the small intestine, the drug molecules were released from the nanoparticle and 24.8 percent of the drug was absorbed [credit: Haifa Shen, Houston Methodist].
“This was just the first drug we tested. Our approach could be used to deliver many other biological drugs, such as human growth hormone and therapeutic antibodies,” said Shen.
Now that the nanomedicine researchers have proven the drug platform works in animal models, the next step is to perform toxicity studies, produce the drugs in a larger quantity and eventually move to clinical trial in patients. However the researchers emphasise that although triglyceride fatty acids may one day be key to fighting diabetes, the technology still has to be developed further before people can derive benefit from consuming fatty acids.
The study was published in Science Advances.
Related topics
Drug Delivery Systems, Formulation, QA/QC, Research & Development (R&D)