RemeGen receives ODD for myasthenia gravis treatment
The FDA has granted ODD to Telitacicept, produced by RemeGen, for the treatment of myasthenia gravis.
RemeGen has announced that the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted Orphan Drug Designation (ODD) for its proprietary novel fusion protein Telitacicept (RC18) for the treatment of myasthenia gravis (MG).
Telitacicept is a proprietary novel fusion protein from RemeGen to treat autoimmune diseases. It is constructed with the extracellular domain of the human transmembrane activator and calcium modulator and cyclophilin ligand interactor (TACI) receptor and the fragment crystallisable (Fc) domain of human immunoglobulin G (IgG). Telitacicept targets two cell-signalling molecules critical for B-lymphocyte development: B-cell lymphocyte stimulator (BLyS) and a proliferation inducing ligand (APRIL), which allows it to effectively reduce B-cell mediated autoimmune responses implicated in several autoimmune diseases.
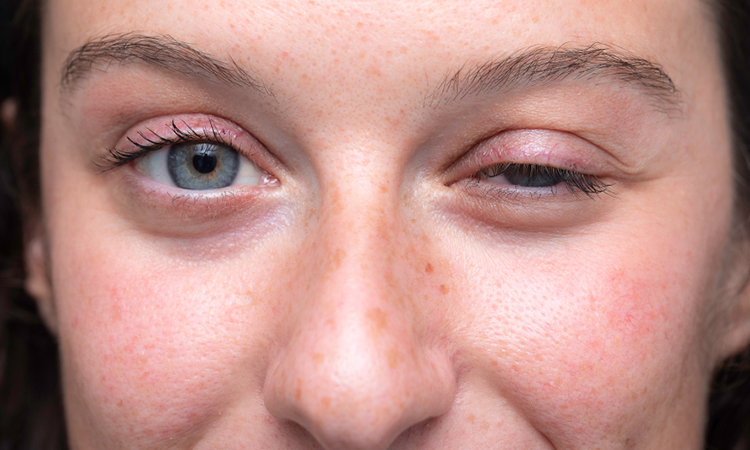
MG is a chronic autoimmune neuromuscular disease that causes patients to be prone to fluctuating muscle weakness. It can affect eye movements, swallowing, speech and respiratory functions; it can even be life-threatening in severe cases. While rare, the disease is a long-term condition that currently is difficult to cure.
At present, the most common treatments for MG include: cholinesterase inhibitors, glucocorticoids, immunosuppressants, intravenous immunoglobulin, plasma exchange, anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) and thymectomy. These treatments come with possible side effects and while fast-acting, treatments such as plasma replacement may have an impact on the immune system. Due to the removal of other macromolecules and poor accessibility a large unmet clinical need is currently being addressed by RemeGen.
RemeGen, in the first quarter of this year, announced the completion of a Phase II clinical study of Telitacicept for the treatment of MG in Chinese patients, which showed positive results.
“We are delighted that the FDA has granted ODD for the RemeGen created proprietary novel fusion protein Telitacicept,” said Dr Jianmin Fang, CEO and Chief Scientific Officer of RemeGen. “This is an important step in our quest to address the large unmet need on a global scale for MG and follows on from our successful Phase II clinical study on patients in China earlier this year.”









What an enjoyable read!