New NHS cell and gene therapy centre opens
Posted: 10 March 2023 | Catherine Eckford (European Pharmaceutical Review) | No comments yet
The new Clinical Biotechnology Centre (CBC) in Bristol will manufacture cell and gene therapies to help boost the UK life sciences sector.


Today marks the opening the NHS Blood and Transplant (NHSBT)’s new Clinical Biotechnology Centre (CBC) in Bristol. The state-of-the-art facility was part-funded by a £9.43 million Government grant and is designed to expand the UK’s ability to manufacture new gene and cell therapies.
The CBC will help the UK grow its cell and gene therapy industry in a rapidly growing international market.”
“The CBC will help the UK grow its cell and gene therapy industry in a rapidly growing international market. We won’t be designing the treatments but we will be manufacturing them to the right scale and clinical grade,” Dr Lilian Hook, NHSBT’s Director of Cell, Apheresis and Gene Therapies explained.
At present, there is insufficient manufacturing at the scale for organisations wanting to undertake early phase biotherapy clinical trials.
The shortage of UK manufacturing capacity means long delays for developers of gene therapies while they wait for production slots. Instead, researchers need to outsource from manufacturers overseas. This inevitably delays clinical trials and patients’ access, and often increases costs.
The Clinical Biotechnology Centre
The Clinical Biotechnology Centre replaces a smaller unit in nearby Langford. Larger commercial sites do exist, which are cost effective for making products for proven treatments. Researchers require access to flexible sites where treatments still being researched and clinically tested can be made cost-effectively in smaller amounts.
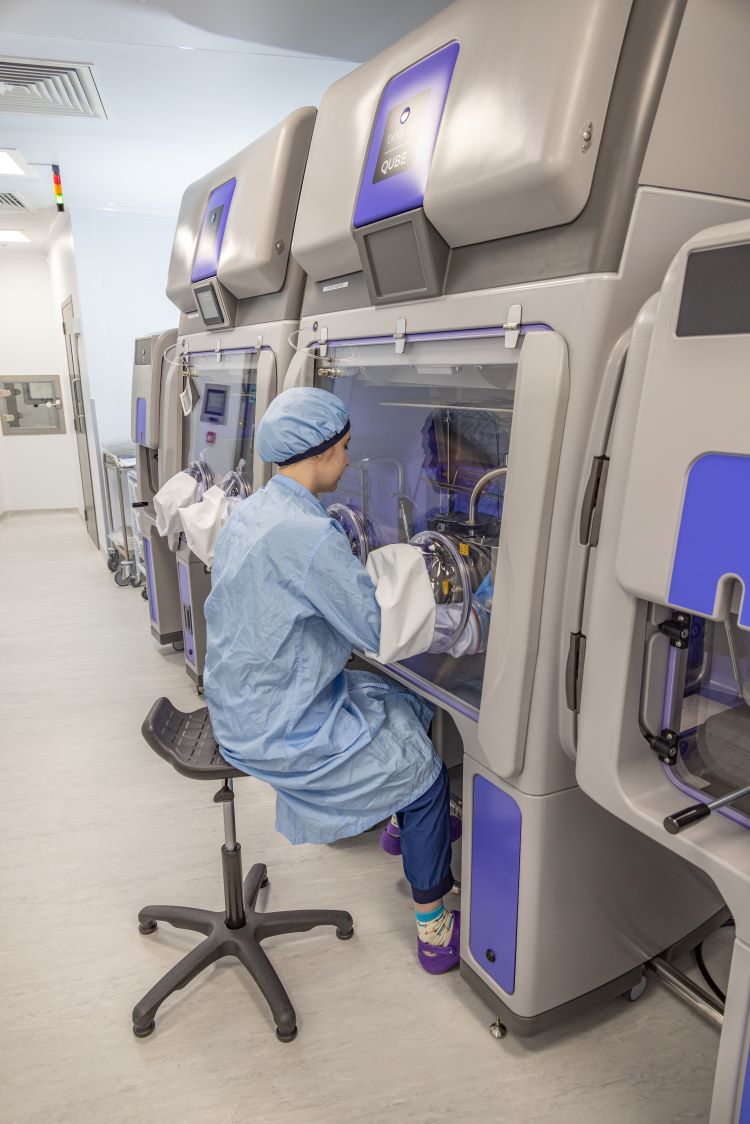

Credit: NHS Blood and Transplant
The CBC will produce:
- Plasmids – these are small fragments of DNA. These can be engineered to introduce gene(s) of interest into cells. The plasmids may be used for direct vaccination of patients (eg, for HIV infection), cell therapies, or as the starting material for viral vectors
- Viral Vectors, which are viruses that have been modified to deliver DNA into cells. They are commonly used in gene therapy for cell re-programming for a therapeutic effect
- Recombinant proteins are proteins with DNA combined from two or more sources. They are made by cells whose DNA has been altered and have a wide range of uses including as medicines.
The centre will help patients have quick access to the latest treatments by increasing the number of UK patients with incurable diseases who are able to take part in clinical trials.
The new facility will produce products for potentially curative therapies for currently incurable diseases, such as some forms of cancer, sickle cell disease, and cystic fibrosis. In gene therapies such as Libmeldy, used to treat metachromatic leukodystrophy, the faulty DNA is replaced, inactivated, or repaired, stated NHS England.
“The CBC is basically a factory – it manufactures the building blocks (or components) needed to produce gene therapies. Researchers and developers can ask us to manufacture the specific components they require,” Dr Hook concluded.
Related topics
Anti-Cancer Therapeutics, Biologics, Biopharmaceuticals, Clinical Trials, Drug Manufacturing, Drug Supply Chain, Gene therapy, Manufacturing, Personalised medicine, Production, Research & Development (R&D), Therapeutics
Related organisations
NHS Blood and Transplant (NHSBT) Clinical Biotechnology Centre (CBC)