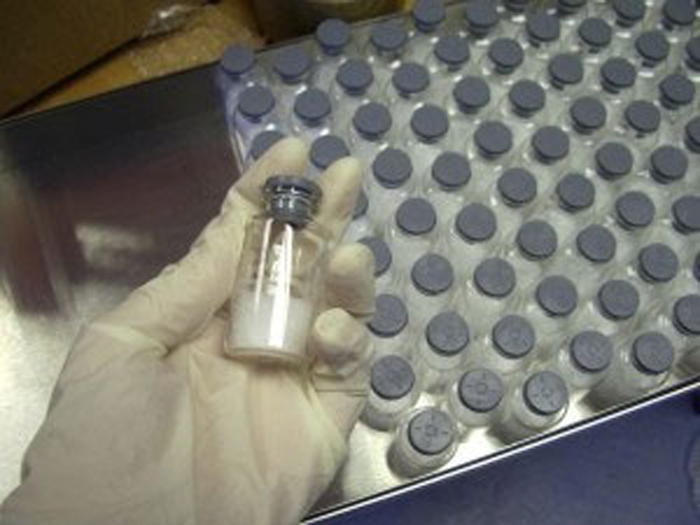
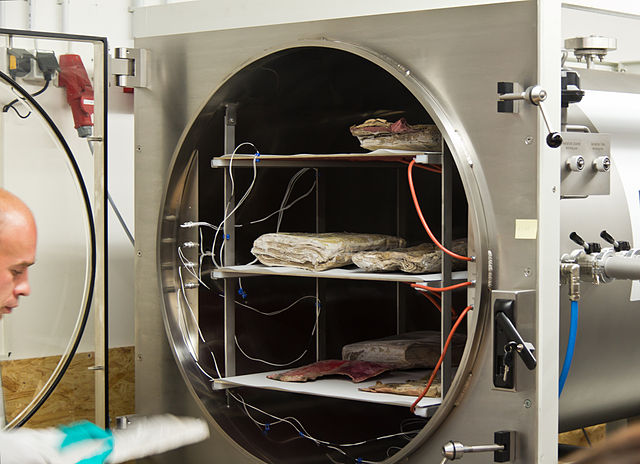
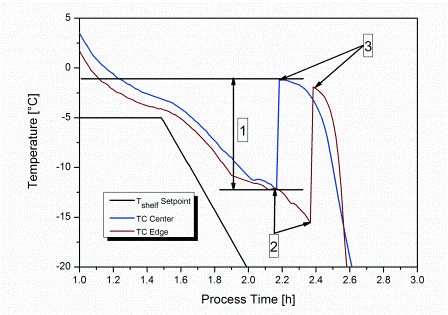
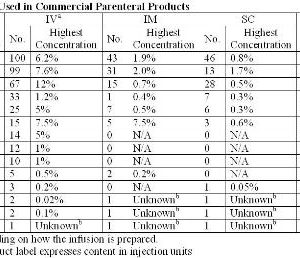
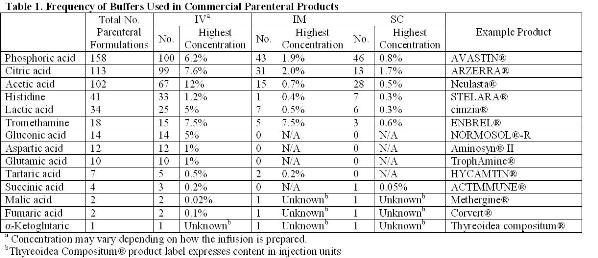
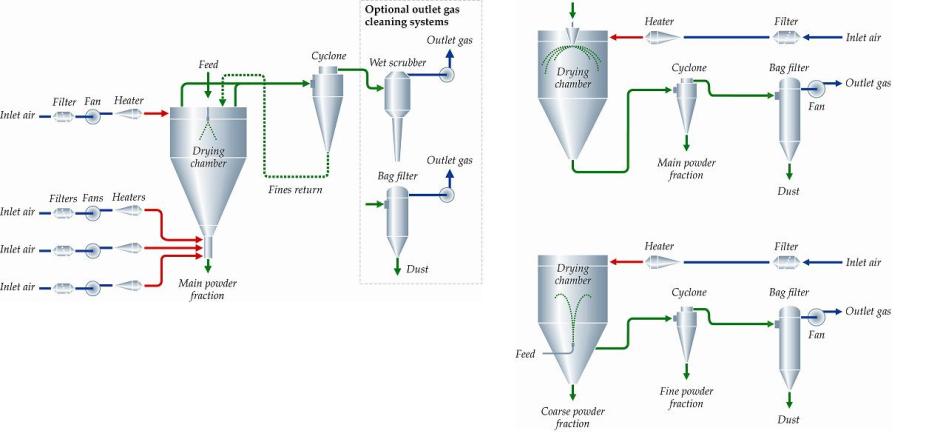
Preserving blood – why we need to look at new options
Blood transfusions have been used successfully since the early 1900s, and blood banks have been in use since 1914. After donation, whole blood is separated into several components for processing and storage under different conditions, and one of these components is the red blood cell fraction.