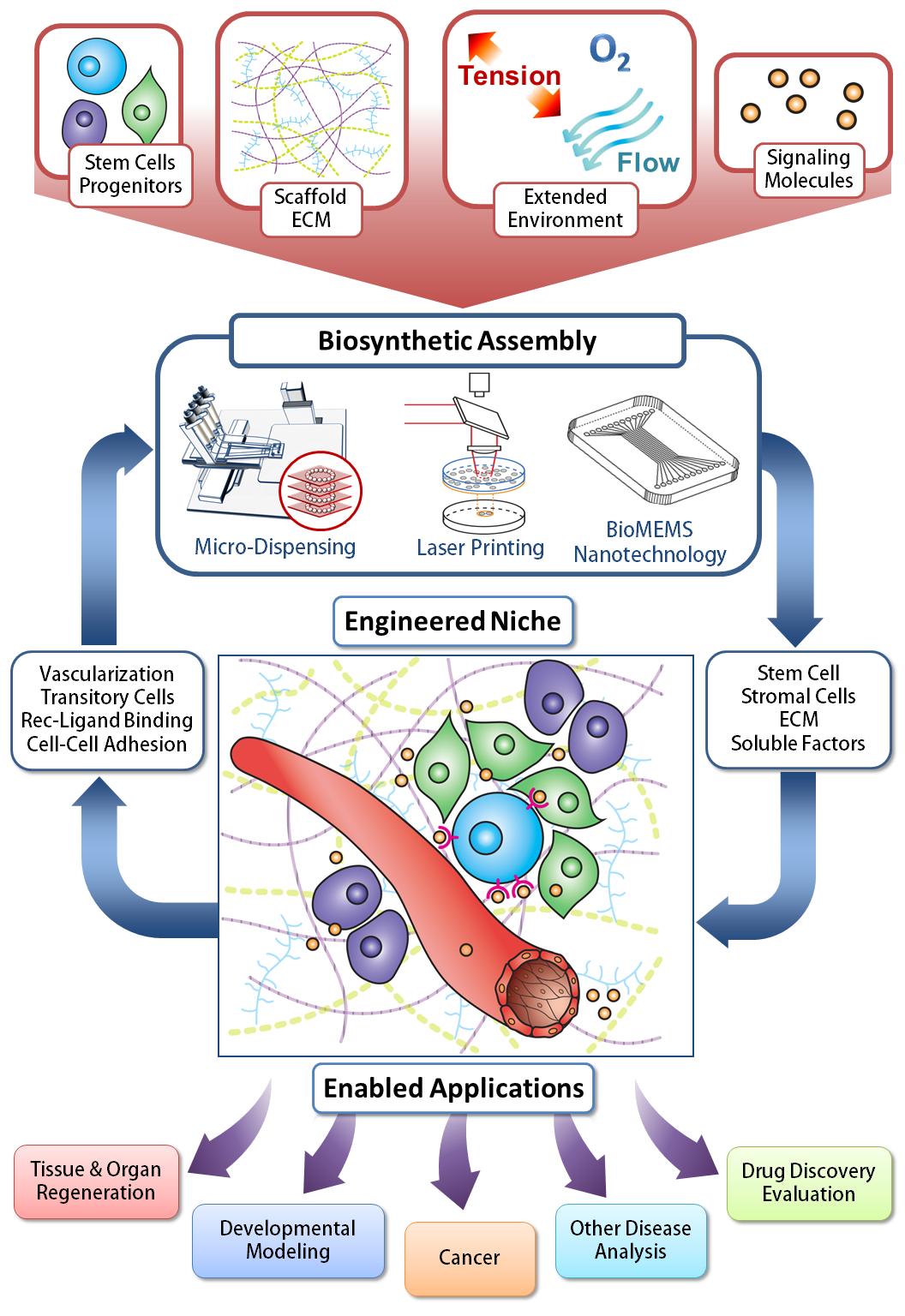
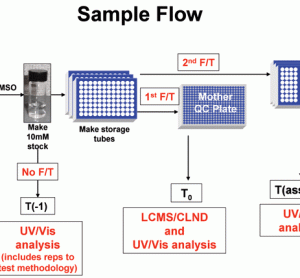
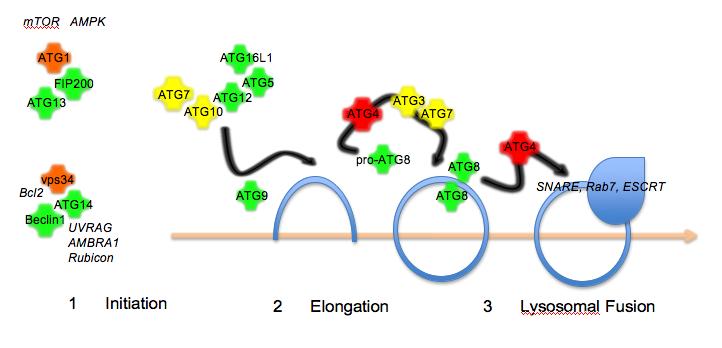
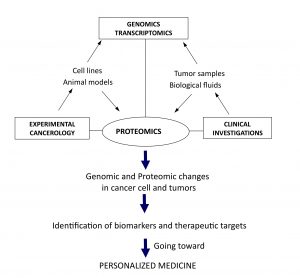
Isothermal titration calorimetry and thermal shift assay in drug design
20 June 2011 | By Asta Zubrienė, Egidijus Kazlauskas, Lina Baranauskienė, Vytautas Petrauskas and Daumantas Matulis, Department of Biothermodynamics and Drug Design, Vilnius University Institute of Biotechnology
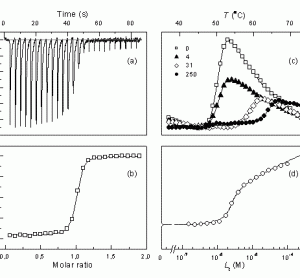
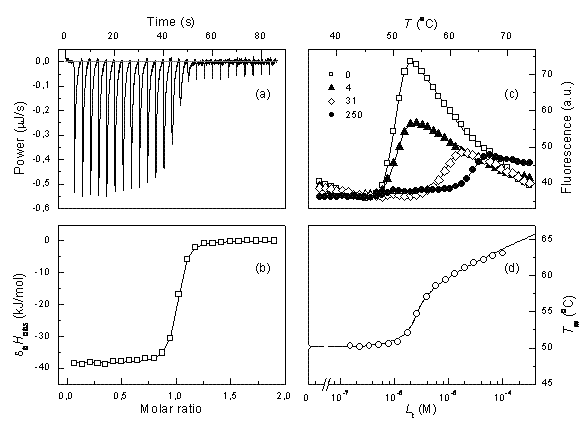
Isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) is a method of choice in the pharmaceutical industry for determination of equilibrium binding enthalpy, entropy, and the Gibbs free energy. The method is very powerful for determination of intrinsic binding parameters that could be used in structure-energetics correlations. Here we discuss how to overcome several…