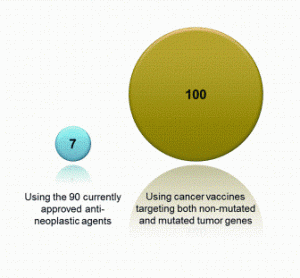
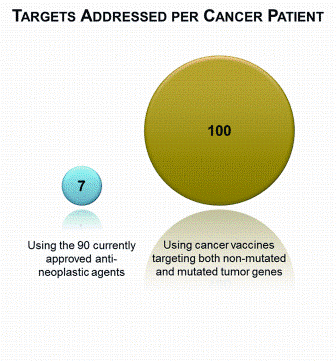
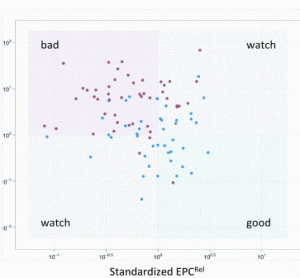
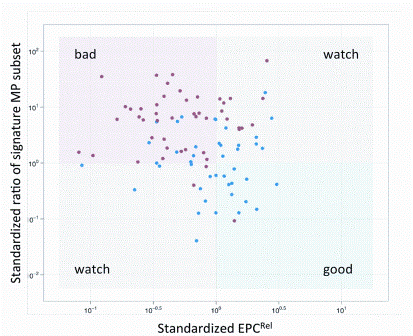
Evolving landscape of pharmaceutical outsourcing in China
22 October 2012 | By Xiaorong He, Senior Research Fellow, Boehringer-Ingelheim
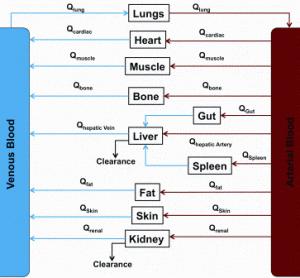
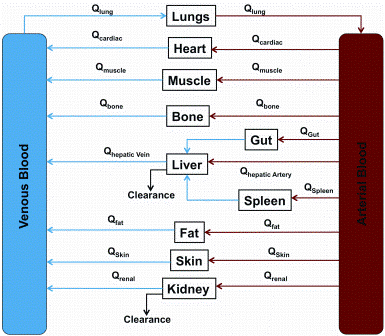
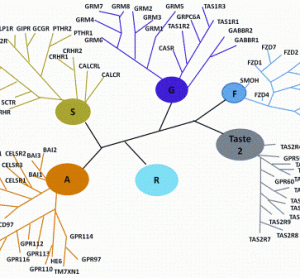
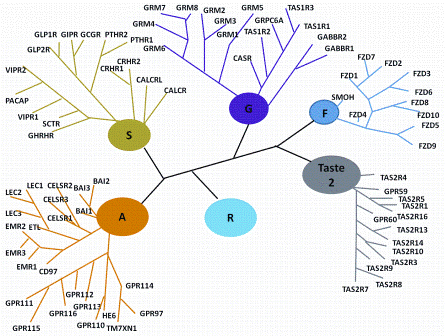
China’s economic growth has shocked and awed the world, with its GDP growing at an average rate of 10 per cent for 30 years. The astonishing economic growth has also spurred rapid growth of pharmaceutical outsourcing business in China. In the past, China had been the major source of raw…